Be prepared - A complete guide to survival in extreme situations.Introduction: At a time when the security environment is increasingly burdened and the nightmare of a war beyond the regional conflict e.g. It is good to know some basic things about how we and our family will survive, especially if we live within an urban fabric.
The collapse of the internal security forces is very likely or their inability to act if communication centers, administration and control are hit.
Defense
Things
Security organization
Information
Internet, television, radio will probably not exist . You need to set up an information flow network with alternative media. Find radios and build antennas that can receive shorts.
Hygiene
Hygiene is very important, as is having adequate medication - especially antibiotics. Painkillers and antipyretics are essential. Gauze, cotton and antiseptics in abundance
Food
Make sure you have stocks of food that can withstandin time with canned food, dry food, etc. Look for a list of items that the Army keeps in stock. It's the best guide to your stocks. Always have a carton in your warehouse and renew it from time to time. You may never need it. You will have lost around 100 euros enough to feed a family of four for a week. If you do not have it, the whole family can be lost ...
Water
Problem. Probably the biggest problem if the water network is contaminatedof your city. There must be a stock of dozens of renewable water bottles here. Look for sources or make sure you get a device that converts seawater into drinking water. If you have a tank, be sure to throw special antiseptic "balls" that they use in the water tanks of ships.
These and ... good luck! News section defencenet.gr http://www.pronews.gr/
More details
1. MATCHES
You should treat safety matches and not the usual matches that can light up anywhere. But you can also turn them into security by dipping their heads in melted wax. To save space, break half a stick from each match.
It's much easier than anything else to light a match with matches, but you should not waste them. Use them only when you fail to light a fire in some other casual way. Take only one match from the box and re-close the lid immediately. Never leave the box open or on the ground.
2. CANDLE
The candle is really very valuable for lighting a fire, just like a fire source. You have to scrape it and straighten it until it gets the right rectangular shape to fit in the can. If it is made from animal fat it can be eaten -because it is greasy- in case of need or used for frying. But make sure it is an animal fat wax. Paraffin wax and some other types of wax are unsuitable for eating. Animal fat wax melts easily in hot climates.
3. FLASH STONES Flint stones
can be used for quite a long time even when there is moisture and you have run out of matches.
Buy processed flint with a serrated lighter (percussion).
4. MAGNITING LENS
You can light a fire directly from the sun's rays. It is also useful in searching for wood spikes that have entered your skin or insect bites that have stung you.
5. NEEDLES AND THREAD
You need several needles and among them necessarily one with a very large eye, so that thick threads can pass through it. Choose a thick thread and wrap it around the needles.
6. HOOKS AND COUPLINGS
You need to have a set of hooks of different sizes in a small box or package. Add a few weights. Remember that a small hook can catch both large and small fish. On the contrary, a large hook only catches large fish. Also get as much line as possible, which may be useful even when catching birds.
7. COMPASS
A small fluorescent compass is the most suitable, but first make sure that it is good, because some of them are completely useless. The liquid compass is the best type, but before you buy it you should check if it is leaking, if it has bubbles and especially if it is easy to use. The indicator needle rusts easily. Make sure it is on its axis of rotation and that it rotates freely.
8. "BETA" LIGHT
It is a crystal that emits light. It is the size of a small coin and is ideal for reading a map at night and useful for fishing bait. It is expensive but indestructible.
9. WIRELESS LOOP
Preferably brass wire loop 60 to 90 cm long.
Be careful with the loops because they can catch you, but on the other hand they can solve many survival problems. ,
10. FLEXIBLE SAW
These usually have large rings on the edges that serve as handles. These rings take up a lot of space for this and you have to take them out of the saw. When you are going to use it you can replace the rings with small wooden pins. To protect the saw from rust and breakage it should be covered with a thin layer of grease. Flexible saws can be used to cut even large trees.
11. MEDICINE BOX
This will include all the medicines you deem necessary. Pack the medicines in airtight boxes with medicated cotton so that
12. SURGICAL BLADES
At least two scalps of different sizes. You can make a wooden handle if needed. "
13. WOUND SEWING TIZERS
Used to join the edges of wound wounds.
14. PLASTICS
Various types, preferably waterproof. They help in small cuts but also in wounds of larger wounds. see. Sewing trauma chapter Health).
15. condom
is a great bag that can hold up to a liter of water.
emergency materials
HEALTH
AVOIDANCE OF FREEZING
LIGHTING A FIRE
We do not light a fire:
1) In a landscape that we have not cleaned from flammable materials (ideally perimeter 6 m.), These materials can be dry grass, dry wood, garbage, under trees, flammable liquids, etc. .
2) In enclosed spaces without proper ventilation
3) In places where we can not control the flame,
4) In places that cause problems in the fauna and flora,
5) In places where we destroy private-public-cultural properties,
6) If we have no way to extinguish it before leaving,
7) If we do not have a plan in case of spread, we must have some means to extinguish it such as water, soil or fire extinguisher
8) If there is no one to look after it on a permanent basis
9) When we cause a noticeable problem to someone, such as "choking" from the smoke
Make a lighter and protect it all around with other wood that will form a triangular wooden frame . If it is blowing, place the lighter on the opposite side of the air, perpendicular to a large piece of wood. Turn on. Once you get it, throw thicker wood or take a hug of dry branches no bigger than matchsticks, light the first ones and throw them in the frame.
MATCHES
Matches are the easiest way to light a fire. Take as many matches as possible with the ones that light up anywhere. Stack them in waterproof boxes so that if they are rubbed or moved, they do not ignite suddenly. The waterproof packaging protects them from both.
Some cut their matches in two. It is said that they can be cut in all six. But do not risk it. It is better to have one to light than six damaged.
Light the cut matches by holding the finger and pressing the functional end against a surface. If the finger burns, cool it with cold water or ice or even spit it out or blow it.
 ATTENTION The issues of SURVIVAL are too many and we present them briefly *, except for Water which is the most important issue and you can see it in the following extensive article. we also do not mention in detail the armament * and the protection from poisonous * and radioactive * gases because it is off-topic * of the blog but you can read them in the free books that we attach
ATTENTION The issues of SURVIVAL are too many and we present them briefly *, except for Water which is the most important issue and you can see it in the following extensive article. we also do not mention in detail the armament * and the protection from poisonous * and radioactive * gases because it is off-topic * of the blog but you can read them in the free books that we attach

As this topic is probably the most important object of survival we will make a short article with basic facts that we all need to know about water in survival situations. As you may already know, a person can live for tens of days without food (for example, David Blaine lived 44 days with only water, read more here ) but not more than a few days without water. With the data known so far we know that no human being can live without water for more than 7 days with more realistic data being between 3 to 5 days.

You automatically realize the severity of water intake under any circumstances, although this varies depending on the situation (climate, fluid loss, fatigue, etc.). The US Department of Defense stipulates that the minimum amount of water intake is 2 liters per day. Caution! This is the minimum, not the recommended. The simplest and fastest method of analysis of possible dehydration, which is something very good for our health and in our daily life, is the color of urine. Excess water is excreted from the urine, among others. So the more transparent their color is, the more water there is and therefore the better hydrated we are. Otherwise, that is, in urine with a darker color, it means that we do not get enough water. As a simple general dehydration guide we can keep in mind the following color chart.
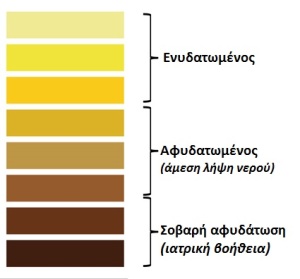
In addition, there are some fluids that cause more dehydration or infections (which then cause dehydration due to fluid loss). Consequently, the following should be avoided because they aggravate the situation. You should not drink:
Source https://defensegr.wordpress.com/
 In extreme survival situations everyone suggests short-term survival kits, we will break the established and suggest in your survival kit to include long-term survival items such as small farm tools such as small pickaxe, spade shovel, split saw (initially can be used for cutting and for defense) , but later in combination with a set of SEED PACKAGE of all kinds can be the key to surviving away from dangerous urban centers.
In extreme survival situations everyone suggests short-term survival kits, we will break the established and suggest in your survival kit to include long-term survival items such as small farm tools such as small pickaxe, spade shovel, split saw (initially can be used for cutting and for defense) , but later in combination with a set of SEED PACKAGE of all kinds can be the key to surviving away from dangerous urban centers.
Free Crisis Survival Books

 Note : All books exist as links on the website and do not "belong" to www.ftiaxno.gr. and at http://bio-aroma.blogspot.gr/
Note : All books exist as links on the website and do not "belong" to www.ftiaxno.gr. and at http://bio-aroma.blogspot.gr/
Most are offered free of charge by foreign or Greek digital libraries, Universities, organizations, or by their creators and are for personal use only. The books are for information only and the website is not responsible for their content. If any of the book links do not work and do not refer you to this book, please let me know by sending a message here, or by email to ftiaxnw@gmail.com , to check it out. How to survive financially
Overcome the Financial Crisis! The times are so difficult that we have to download ideas to survive.
General Survival
3 Day Emergency Preps
72 Hour Supplies
All Hazard Preparedness Workbook
Common Sense Guide To Being Prepared
Compact Survival Kit
Complete Worst Case Scenario
Disaster Handbook
Emergency Preparedness Checklist
Emergency Preparedness Manual
Emergency Supplies Checklist
FEMA - Are You Ready?
FRC Preparedness Handbook
How to Prepare for Any Disaster
LA Fire Department Emergency Preparedness
Mini Urban Survival Kit
National Security Emergencies
Ragnar’s Urban Survival
Surviving in the City
Communication
Bass Pro Shop Radio Guide
Best Buy FRS Radio Guide
Disaster Communications
Disaster Communications 2
Hams to the Rescue
How to Buy a Two Way
Radio Amateur's Handbook
Radio Info
Reconnecting After Disaster
Shortwave Radio 101
Shortwave Radio Handbook
Survival Communication 101
Survival Communications Primer
Cook Books
Belgian Cook Book
Cloud City Cookbook
Genesee Valley Cookbook
Kenton Cookbook
Modern Women of America Cookbook
Most For Your Money
Native American Health Recipes
Pleasantville Cook Book
Riverside Recipe Book
Second Parish Cookbook
Vegetarian Cook Book
Westminster Cook Book
Cooking Methods
Base Camp Trail Stove
Bush Fungus Stove
Double Drum Sawdust Stove
Emergency Bread
Food Bucket Stove
Rocket Stove
Sawdust Burning Stove
Energy, Fire, Light
Biodiesel Safety
Bow Drill
Cheat Solar Power
Choosing a Back Up Generator
Emergency Power Options
Fighting Fire
Fire by Can
Generator Sizing WP
Getting Started In Solar
Homemade Windmills
How Much Is Enough
Making Charcoal
Power Outage Checklist
Solar Power
Solar Water Heater
SunWize RVkits specsheet
Tinder Fungus
Water Proof Matches
Food and Storage
3 Month Supply Of Food
Emergency Food and Water
Emergency Food for Babies
Emergency Preparedness Food
Family Food Storage
Food Storage for 1 Year
Food Storage for Survival
Food Storage Guide
Food Storage in the Home
Food Storage and Rodents
Get Ready Now
Grain Dehuller
Grain Thresher
Grains And Legumes
Growing and Harvesting Wheat
Hand Operated Winnower
Improvised Grain Mill
Keeping Food Safe to Eat
Mylar Bag Sealing Methods
One Year Emergency Food Supply
Peddle Operated Grain Mill
Plant Identification
Preserving Vegetables
Shelf Life of Food Storage
Stocking Food
Stocking For Small Spaces
Storage of Wheat
Survival Food Storage
TACDA Emergency Food and Water
Vacuum Packing Seed
Gardening
A Better Way to Gardening
Amateur Garden
Building a Hydroponic Garden
Container Gardening 1
Container Gardening 2
Container Gardening Vegetables
Growing Container Vegetables
Growing Mini Gardens
Growing Sweet Corn
Growing Vegetables at Home
Growing Vegetables Basics
Growing Vegetables from Seed
Growing Vegetables in Containers
Keeping Food Safe in an Emergency
NC State - Growing Vegetables
NC State - Home Vegetables
Raised Bed Gardening
Short Season Vegetable Gardening
SM Space Gardening
Small Plastic Greenhouses
Start a Small Garden
Start a Vegetable Garden
Start Garden Transplants
Vegetable Gardening Encyclopedia
Health, Medical, Sanitation
Animal Bites First Aid
Base Campe Hygiene and Health
Blisters First Aid
Burns First Aid
CPR Instructions
Diabetes Disaster Guidelines
Edible Medicinal Plants
Emergency War Surgery
First Aid For Soldiers
Isolation Planning
Mass Casualty Planning
Medical emergencies
Medical NBC Battlebook
Survival Medicine
Survival Wilderness Medicine
the Using Safe Burial Practices
Wilderness Med Kit
Nuclear, Biological, Chemical
CBR Nuclear War Survival
Chemical emergencies
EMP Commission 7MB
EMP Executive Report Report
Fallout Protection
FEMA CBR Nuclear War Survival
FEMA Nuclear Survival
Nuclear War Survival Skills
Nuclear Weapons Effects
Radiological Defense Preparedness
SM-12f Home Fallout Shelter
Threat to US from an EMP Attack
What if Nuclear War is Imminent
Official Manuals
Canada CD Notebook
Canada CD Operations
Canada CD Public Information
FM 3-06 Urban Combat
FM 3-3-1 Nuclear Contamination
FM 3-4 NBC Protection
FM 3-5 NBC Decontamination
FM 3-9 Chemical / Biological
FM 3-11-4 Mulitiservice Tactics
FM 4-02 Nuclear Casualties
FM 4-25-11
FM 5-20 Camouflage
FM 7 NBC Field Handbook
FM 8-50 Bandaging
FM 8-284 Treatment of Casualties
FM 21-10 Field Hygeine
FM 21-11 First Aid for Soldiers
FM 21-75 Combat Skills
FM 21-76 Survival Manual
FM 21-150 Combatives
FM 90-10-1 Combat
US Army Dairy
United States Marine Survival
US Marine Corps MCRP 3-02F
US Marine Corps MSVX.02.01
Self Defense, Weapons
Choosing a Weapon
Citizen’s Homeland Defense Guide I
Citizen’s Homeland Defense Guide II
FN High Capacity 45
G&A SR9
Glock Versus M1911
Homeland Defense 45
Military Operations On Urbanized Terrain
Smith & Wesson Sigma SW9VE
Springfield XD Review
Ruger SR9
Stag Review
Survival Guns
Survival Weapons
Tactical Ready Guide
Shelter
Basement Shelter
Build a Fallout Shelter
Build a Shelter
Home Shelter Above Ground
Home Shelter Outside Concrete
Shelter Management Handbook
Shelters
Survival Wilderness Shelter Types
Taking Shelter
Wilderness Shelter Types
Water
Emergency Disinfection of Water
Emergency Water Purification
Priming the Berkey Filter
Purification Of Water On A Small_Scale
Purify Water in an Emergency
Solar Photovotaics
Solar Water Heater
Water Survival Course
Water Treatment
Wind Machine for Pumping Water
Miscellaneous
Art and Science of Dumpster Diving
BOB Survival Kit
Bug Out Bag
Bug Out Vehicle Basics
Desert Survival
Earthquake Preparedness Guide
Earthquake Tips
Get Out Of Dodge
Handbook of Knots and Splices
How to Avoid Getting Lost
How To Find Your Way
Knots For Camping Climbing Utility
Pioneering Knots and Lashings
Poisonous Plants
Wilderness Survival Techniques
Winter Survival
Winter Survival In Your Car
Read more: Free books for materials and constructions
http://www.parnitha‐np.gr/oreivasia.htm
http://www.hellaspath.gr/index.php? p = 2
The collapse of the internal security forces is very likely or their inability to act if communication centers, administration and control are hit.
Antiseptics, detergents, soap, gloves, masks.
In a state of war, hygiene items and medicines are more important than food. You can shoot a dove. You can cut a plant to eat. But you can neither shoot nor plant an antiseptic. Collect antiseptics, detergents, soap, gloves, masks.
In a state of war, hygiene items and medicines are more important than food. You can shoot a dove. You can cut a plant to eat. But you can neither shoot nor plant an antiseptic. Collect antiseptics, detergents, soap, gloves, masks.
First aid
Learn to give first aid, clean wounds and take care of burns. Even if you find a doctor, you may not be able to pay him. Learn to use antibiotics. It is good to have stock.
Learn to give first aid, clean wounds and take care of burns. Even if you find a doctor, you may not be able to pay him. Learn to use antibiotics. It is good to have stock.
Defense
- You should choose to have as simple weapons as possible and make sure you have legally acquired firearms and lots of ammunition, even shotguns, preferably semi-automatic for basic protection. The Russian Saiga and Molot, but also many American rifles do an excellent job.
- It is good for as many members of your family as possible to use their weapons. You never know who will have to shoot or aim with an improvised weapon to save you or a family member.
- How difficult is it to find weapons and ammunition? You can make ammunition supplies in peacetime. Remember that the hardest hours are in the early days, so if you do not already have weapons and ammunition, you may not have enough time to acquire them and protect your family. Being unarmed in a state of turmoil is a very bad idea.
- How much ammunition? As many as possible.
Things
- You need to have small things that do not catch the eye. For example, a generator is good, but 1,000 BIC lighters are better. The generator will attract attention in case of a problem, while the lighters are small, cheap and easily interchangeable.
- Are gold and silver useful? Yes, because you can trade them for food, medicine, water, weapons and ammunition.
- Do not wear valuables in such times and situations. Someone will kill you to get them. Even your behavior should not stand out.
Security organization
- Organize the perimeter of your home. Chaotic situations may prevail. The hundreds of thousands of illegal immigrants, either because they will be hungry and desperate or because they will play the role of the 5th phalanx, will be a major threat to security, as well as anti-social and delinquent elements of society.
- Make sure no one has visual access to the interior of your home, especially if you live in a detached house.
- Try not to target the house , do not look fortified. The fortified house shows that it has something to hide. Make sure you have defense teams organized by friends and relatives. If disaster struck and you live in the city, you need a simple, not at all fancy place, full of weapons and ammunition.
- Prepare an escape plan in the countryside. It is important that you and your family survive. The houses are being rebuilt and the furniture is being bought. Your lives, no.
- Security supersystems and super weapons are useless. If someone thinks it's worth stealing your stuff, they will try to do it over and over again. It's only a matter of time and firepower, so you want weapons, ammunition and hands.
- It is important that a self-defense force has been organized in your neighborhood since peacetime . Always organized watchtowers and patrols outside in the streets. Good organization and coordination are essential for protecting against gangs.
Information
Internet, television, radio will probably not exist . You need to set up an information flow network with alternative media. Find radios and build antennas that can receive shorts.
Hygiene
Hygiene is very important, as is having adequate medication - especially antibiotics. Painkillers and antipyretics are essential. Gauze, cotton and antiseptics in abundance
Food
Make sure you have stocks of food that can withstandin time with canned food, dry food, etc. Look for a list of items that the Army keeps in stock. It's the best guide to your stocks. Always have a carton in your warehouse and renew it from time to time. You may never need it. You will have lost around 100 euros enough to feed a family of four for a week. If you do not have it, the whole family can be lost ...
Water
Problem. Probably the biggest problem if the water network is contaminatedof your city. There must be a stock of dozens of renewable water bottles here. Look for sources or make sure you get a device that converts seawater into drinking water. If you have a tank, be sure to throw special antiseptic "balls" that they use in the water tanks of ships.
These and ... good luck! News section defencenet.gr http://www.pronews.gr/
More details
- A few basic species can help you significantly in your quest for survival.
- Everything can be placed in a small metal box , e.g. a canister of tobacco that does not bother you at all when you put it in the pocket of a jacket.
- Make it a habit and always carry it with you. Do not choose something bigger, because it is very likely that it will prove to be completely unsuitable for transport and will be forgotten in cases where it is necessary.
- Many people who roll cigarettes have such boxes. But the box we are talking about is much more useful because it can help you save your life. On the contrary, the smoker shortens his own life.
- Experience has shown that each of these items is very useful, but some are more useful in specific cases. For example, fishing hooks, while valuable for the jungle, have no value in the desert.
- Polish the inside of the canister to create a mirror-like surface that reflects the sun's rays. Then seal the box to make it waterproof with a piece of adhesive tape so you can remove or replace it. Of course never forget its contents. At regular intervals you should check mainly for those that have a limited shelf life, such as matches and medications. Note on the boxes containing medicines their use, dosage and expiration date, at which time they should be replaced. Fill the spare part of your box with medicated cotton which will prevent the contents from being moved, but can even be used to light a fire.
SURVIVAL (BASIC SURVIVAL EQUIPMENT
1. MATCHES
You should treat safety matches and not the usual matches that can light up anywhere. But you can also turn them into security by dipping their heads in melted wax. To save space, break half a stick from each match.
It's much easier than anything else to light a match with matches, but you should not waste them. Use them only when you fail to light a fire in some other casual way. Take only one match from the box and re-close the lid immediately. Never leave the box open or on the ground.
2. CANDLE
The candle is really very valuable for lighting a fire, just like a fire source. You have to scrape it and straighten it until it gets the right rectangular shape to fit in the can. If it is made from animal fat it can be eaten -because it is greasy- in case of need or used for frying. But make sure it is an animal fat wax. Paraffin wax and some other types of wax are unsuitable for eating. Animal fat wax melts easily in hot climates.
3. FLASH STONES Flint stones
can be used for quite a long time even when there is moisture and you have run out of matches.
Buy processed flint with a serrated lighter (percussion).
4. MAGNITING LENS
You can light a fire directly from the sun's rays. It is also useful in searching for wood spikes that have entered your skin or insect bites that have stung you.
5. NEEDLES AND THREAD
You need several needles and among them necessarily one with a very large eye, so that thick threads can pass through it. Choose a thick thread and wrap it around the needles.
6. HOOKS AND COUPLINGS
You need to have a set of hooks of different sizes in a small box or package. Add a few weights. Remember that a small hook can catch both large and small fish. On the contrary, a large hook only catches large fish. Also get as much line as possible, which may be useful even when catching birds.
7. COMPASS
A small fluorescent compass is the most suitable, but first make sure that it is good, because some of them are completely useless. The liquid compass is the best type, but before you buy it you should check if it is leaking, if it has bubbles and especially if it is easy to use. The indicator needle rusts easily. Make sure it is on its axis of rotation and that it rotates freely.
8. "BETA" LIGHT
It is a crystal that emits light. It is the size of a small coin and is ideal for reading a map at night and useful for fishing bait. It is expensive but indestructible.
9. WIRELESS LOOP
Preferably brass wire loop 60 to 90 cm long.
Be careful with the loops because they can catch you, but on the other hand they can solve many survival problems. ,
10. FLEXIBLE SAW
These usually have large rings on the edges that serve as handles. These rings take up a lot of space for this and you have to take them out of the saw. When you are going to use it you can replace the rings with small wooden pins. To protect the saw from rust and breakage it should be covered with a thin layer of grease. Flexible saws can be used to cut even large trees.
11. MEDICINE BOX
This will include all the medicines you deem necessary. Pack the medicines in airtight boxes with medicated cotton so that
- avoid moving them. The following medications cover most ailments, but are just a simple guide.
- Analgesics. A painkiller for mild to moderate pain. Methylmorphine phosphate is ideal for toothaches, headaches and earaches. Dosage: one tablet every six hours and for as long as needed. Because it causes constipation symptoms it can be used against diarrhea.
- Antidiarrheals. Cure acute or chronic diarrhea. We recommend that you use Imodium. First you take two tablets and then one each time you have a bowel movement.
- Antibiotics. For general infections. Tetracycline can be used even by people hypersensitive to penicillin. Dosage: one 250 mg capsule, four times a day. This should be repeated for five to seven days. Take several capsules with you so that you can cover a full range of days. When taking them, it is advisable to avoid drinking milk, calcium, iron supplements and other medicines that contain aluminum hydroxide.
- Antiallergic. For allergies, bites or insect bites (can be used in side effects from the use of other drugs). Piriton is recommended in Britain and Benadril in the US. A characteristic symptom of the use of Piriton is drowsiness, so it can be used as a light hypnotic. You should not exceed the recommended dosage, nor should you combine it with alcohol.
- Water sterilizing tablets. You should use them when you suspect that your water is contaminated and you can not boil it. Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
- Malaria pills. Necessary mainly for areas where there is malaria. For some of them you can only take one pill a month.
- Potassium permanganate. It has several uses. Add it to the water and when it gets a light pink shade it is sterilized, while when it becomes deeper pink it can be used as an antiseptic. When it is completely red, it helps in the treatment of fungal infections (eg athlete's fungus).
12. SURGICAL BLADES
At least two scalps of different sizes. You can make a wooden handle if needed. "
13. WOUND SEWING TIZERS
Used to join the edges of wound wounds.
14. PLASTICS
Various types, preferably waterproof. They help in small cuts but also in wounds of larger wounds. see. Sewing trauma chapter Health).
15. condom
is a great bag that can hold up to a liter of water.
emergency materials
HEALTH
- There is a high risk of frostbite, hypothermia and blindness from the reflection of the sun in the snow. In addition, efforts to deal with the cold, by blocking air from the shelter, can have unpleasant consequences, such as lack of oxygen and carbon monoxide poisoning.
- It is very easy to escape from reality by lying down with your clothes on and resting your head on a piece of wood. In such a case, even thinking is tedious. But this is not the case. You should always be vigilant, because it is very likely that you will overlook even obvious things. Always be on the move, but do not get tired because you have to keep your strengths for useful tasks. Get as much sleep as possible.
- You will wake up before you freeze from the cold, unless you are completely exhausted, in which case you can not renew the heat lost in the air. Do not lose your morale with the cold. Think of ways to better protect yourself. For example, make a better pair of gloves.
- Exercise your fingers and limbs in general to improve blood circulation. Do not forget to defecate. Often, if you do not pay attention to it, constipation is created in the body. Be regular and even take care before you start from your shelter, so that you do not have a problem on the road.
AVOIDANCE OF FREEZING
- Wrinkle the skin of your face to prevent it from sticking, moving the muscles in every direction. Keep practicing your hands.
- Be prepared both for yourself and for others, lest blisters, redness or blackheads appear on the skin, especially on the face, ears and hands.
- AVOID fitted clothing, as it reduces blood circulation.
- If you have a sleeping bag, wrap it inside which is warm.
- Never go out without being well dressed and always for a while.
- Do not wear wet clothes made of sweat and water.
- If they get wet, then dry them as soon as possible.
- Shake off the snow before entering the accommodation, or leave your snow-covered outerwear a little further in from the entrance.
- The snow will melt with the heat so you will have more clothes available to wear when dry.
- Always wear dry gloves. NEVER touch metals with bare hands.
- AVOID pouring gasoline on naked flesh. At sub-zero temperatures it will freeze almost immediately and do even more damage as the melting point of gasoline is much lower than that of water.
- Be especially careful when you work hard and feel tired. If you do not feel well, REST.
LIGHTING A FIRE
We do not light a fire:
1) In a landscape that we have not cleaned from flammable materials (ideally perimeter 6 m.), These materials can be dry grass, dry wood, garbage, under trees, flammable liquids, etc. .
2) In enclosed spaces without proper ventilation
3) In places where we can not control the flame,
4) In places that cause problems in the fauna and flora,
5) In places where we destroy private-public-cultural properties,
6) If we have no way to extinguish it before leaving,
7) If we do not have a plan in case of spread, we must have some means to extinguish it such as water, soil or fire extinguisher
8) If there is no one to look after it on a permanent basis
9) When we cause a noticeable problem to someone, such as "choking" from the smoke
Make a lighter and protect it all around with other wood that will form a triangular wooden frame . If it is blowing, place the lighter on the opposite side of the air, perpendicular to a large piece of wood. Turn on. Once you get it, throw thicker wood or take a hug of dry branches no bigger than matchsticks, light the first ones and throw them in the frame.
MATCHES
Matches are the easiest way to light a fire. Take as many matches as possible with the ones that light up anywhere. Stack them in waterproof boxes so that if they are rubbed or moved, they do not ignite suddenly. The waterproof packaging protects them from both.
Lighting a fire with magnesium - Magnesium for lighting a fire
Some cut their matches in two. It is said that they can be cut in all six. But do not risk it. It is better to have one to light than six damaged.
Light the cut matches by holding the finger and pressing the functional end against a surface. If the finger burns, cool it with cold water or ice or even spit it out or blow it.
 ATTENTION The issues of SURVIVAL are too many and we present them briefly *, except for Water which is the most important issue and you can see it in the following extensive article. we also do not mention in detail the armament * and the protection from poisonous * and radioactive * gases because it is off-topic * of the blog but you can read them in the free books that we attach
ATTENTION The issues of SURVIVAL are too many and we present them briefly *, except for Water which is the most important issue and you can see it in the following extensive article. we also do not mention in detail the armament * and the protection from poisonous * and radioactive * gases because it is off-topic * of the blog but you can read them in the free books that we attachSURVIVAL: WATER
- Hydration (Journal of Special Forces)
- How important is water? (medNutrition.gr)
- The value of water (Journal of Special Forces)

As this topic is probably the most important object of survival we will make a short article with basic facts that we all need to know about water in survival situations. As you may already know, a person can live for tens of days without food (for example, David Blaine lived 44 days with only water, read more here ) but not more than a few days without water. With the data known so far we know that no human being can live without water for more than 7 days with more realistic data being between 3 to 5 days.

You automatically realize the severity of water intake under any circumstances, although this varies depending on the situation (climate, fluid loss, fatigue, etc.). The US Department of Defense stipulates that the minimum amount of water intake is 2 liters per day. Caution! This is the minimum, not the recommended. The simplest and fastest method of analysis of possible dehydration, which is something very good for our health and in our daily life, is the color of urine. Excess water is excreted from the urine, among others. So the more transparent their color is, the more water there is and therefore the better hydrated we are. Otherwise, that is, in urine with a darker color, it means that we do not get enough water. As a simple general dehydration guide we can keep in mind the following color chart.

In addition, there are some fluids that cause more dehydration or infections (which then cause dehydration due to fluid loss). Consequently, the following should be avoided because they aggravate the situation. You should not drink:
- Tail
- Fish liquids
- Blood
- Salty (sea) water
- Alcoholic beverage
- Snow or ice
As for the latter (snow or ice) it has to do with its temperature. Its low temperature will lower our body temperature forcing us to expend more energy to maintain our body temperature at normal levels. This can eventually lead to dehydration. It can also cause minor injuries to the lips and neck. However, if we melt it first it is a very good source of drinking water. In the following order of priority, the best drinking water sources in the wild according to the U.S. Armed Forces School of Survival are as follows.


- Surface water ( springs, rivers and lakes )
- Precipitation ( rain, snow, humidity, sleet )
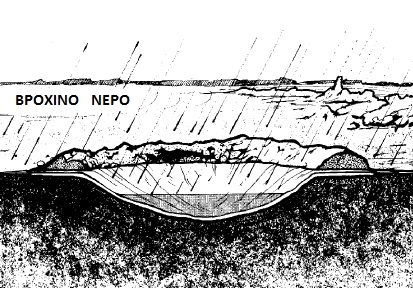
- Basements ( wells and reservoirs )
- On the ground ( if there is no other option ):
- Plenty of rich vegetation
- Channels and low areas
- Usually traces of animals in the same direction indicate the presence of water
- Usually the direction in which birds fly in the early morning or late afternoon leads to water
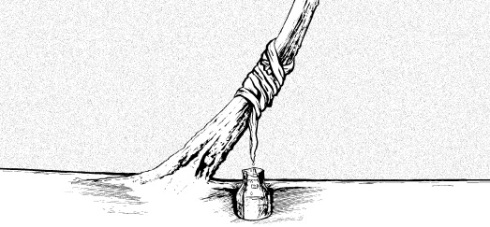
There are literally dozens of ways to collect water in survival mode. In this article we will give you an example of the ways in which the American school of survival is taught. If we have the ability and the climate allows it we can build a rainwater collection system like the one you see here. If we are constantly moving between vegetation with moisture, another technique is to tie an absorbent cloth to our feet to collect water without requiring anything more from us. You can see an example of this in the next image.
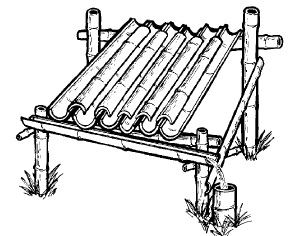
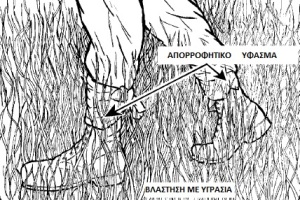
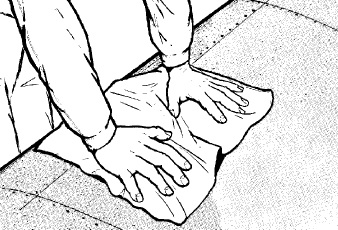
In the same way we can of course collect water from surfaces that allow us to do so. An example of this can be seen below where with a absorbent cloth the soldier collects the water that has been collected from the ambient humidity on a metal surface. And of course we can just place a bag or a raincoat in a hollow spot on the ground during rainfall to collect the rainwater there. We simply fasten with stones the perimeter of the waterproof (or bag or other similar material) as you see in the next picture.
At the beginning of the article we saw a photo of an American soldier drinking water from a tree. This technique is very simple and easy to use in tropical environments. As some woods such as bamboo are hollow and collect both water from the humidity and from the rain if it has rained recently, something very common in tropical climates. As a sketch you can see exactly the same technique here.

By simply shaking and tapping the bamboo wood, one can quickly see if there is water inside or not. It can also be cut and transported as a hermit crab as it holds water inside. Another technique for collecting water from bamboo wood is in a container so as not to alter the environment, something very important if in addition to survival we are in a state of escape in a hostile area. This can be done as you can see below. Caution! We never drink white sap from plants and trees, including bamboo. These juices often cause poisoning which results in diarrhea which causes huge fluid loss and therefore dehydration.

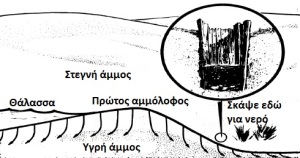
Another technique for tropical climates is to tie a cloth to a tree to collect water from moisture or rain. This method works best on sloping trees but as taught in the US Armed Forces Survival School in a state of escape should be done very carefully, for example near the roots of the tree and with proper concealment. In the tropics it is also very important to know that although coconut has drinking juice, green (unripe) coconuts can cause diarrhea. One last technique for the tropics is to collect water from the shore. The method uses beach sand as a filter as you can see in the next image.
This leads us to another issue, how do we collect water in a state of survival in the sea? The simplest techniques are collecting rainwater and water from the morning moisture. The advantage with surviving at sea is that all the equipment is usually made of plastic materials that can be used to make water collectors as described above. In addition, in icy areas there are two types of ice, the new sea ice and the old. The difference is that the old sea ice is at least a year old and has a very low salt content. Thus, the old sea ice can be used as drinking water if there are no other ways to find water.


In the same way we can of course collect water from surfaces that allow us to do so. An example of this can be seen below where with a absorbent cloth the soldier collects the water that has been collected from the ambient humidity on a metal surface. And of course we can just place a bag or a raincoat in a hollow spot on the ground during rainfall to collect the rainwater there. We simply fasten with stones the perimeter of the waterproof (or bag or other similar material) as you see in the next picture.


At the beginning of the article we saw a photo of an American soldier drinking water from a tree. This technique is very simple and easy to use in tropical environments. As some woods such as bamboo are hollow and collect both water from the humidity and from the rain if it has rained recently, something very common in tropical climates. As a sketch you can see exactly the same technique here.

By simply shaking and tapping the bamboo wood, one can quickly see if there is water inside or not. It can also be cut and transported as a hermit crab as it holds water inside. Another technique for collecting water from bamboo wood is in a container so as not to alter the environment, something very important if in addition to survival we are in a state of escape in a hostile area. This can be done as you can see below. Caution! We never drink white sap from plants and trees, including bamboo. These juices often cause poisoning which results in diarrhea which causes huge fluid loss and therefore dehydration.

Another technique for tropical climates is to tie a cloth to a tree to collect water from moisture or rain. This method works best on sloping trees but as taught in the US Armed Forces Survival School in a state of escape should be done very carefully, for example near the roots of the tree and with proper concealment. In the tropics it is also very important to know that although coconut has drinking juice, green (unripe) coconuts can cause diarrhea. One last technique for the tropics is to collect water from the shore. The method uses beach sand as a filter as you can see in the next image.


This leads us to another issue, how do we collect water in a state of survival in the sea? The simplest techniques are collecting rainwater and water from the morning moisture. The advantage with surviving at sea is that all the equipment is usually made of plastic materials that can be used to make water collectors as described above. In addition, in icy areas there are two types of ice, the new sea ice and the old. The difference is that the old sea ice is at least a year old and has a very low salt content. Thus, the old sea ice can be used as drinking water if there are no other ways to find water.
| Old Ice | New Ice |
| Towards blue or black | White or gray |
| It breaks easily | It does not break easily |
| Round edges | Sharp edges |
| It has an unsalted taste | Intense taste of salt |
But as mentioned above, ice should never be drunk immediately due to its low temperature. One method is to place it in a waterproof container and then close to our body, but not on it. To heat it in some way or with warmer water, etc. The best method that melts the ice-snow and at the same time filters it is the one you see in the next explanatory drawing. Here, however, care is required to stir the water at regular intervals so as not to damage the filter container made of parachute cloth. And now moving to the other end, that is, in areas with high drought there are other techniques with the best known being the following.
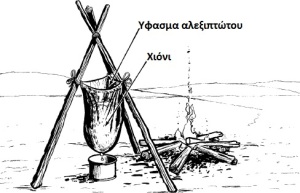
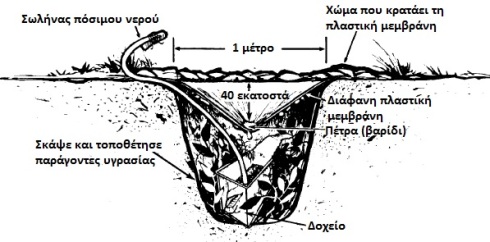
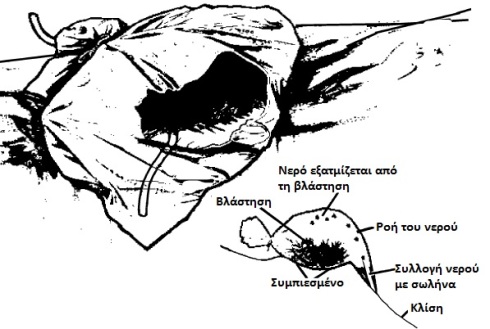
This method is based on the distillation of water using solar radiation. This technique requires the manufacturing process of the above device but can provide drinking water for a long time without any special maintenance. Another method is to collect moisture from the vegetation. You see, we can do that later. The bag must be transparent to allow sunlight to enter. Regarding the pipe, the use of a surgical pipe is recommended and we should know that the water will have a slight taste of the smell of the vegetation from where it came from. In this method we must be careful not to use it on poisonous or toxic plants. In areas with more intense vegetation we can do the same with a tree as you see below.

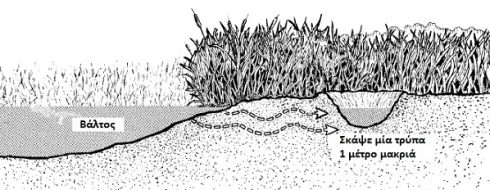
Similar to the technique near shores, we can use natural soil filtration in swamps with the method you see in the image below. Just like water collection techniques, there are just as many techniques for filtering water. The principle is that we want to pass water through porous materials (sand, coals, leaves, etc.) to remove as much as possible harmful particles as possible. Always, the safest method is to boil the water for at least one minute.

The issue of water in survival is a matter of the utmost importance and the more we know the better our chances of survival. As in all subjects, theoretical knowledge without practice and repetition has very little value. So, if you are interested in this subject, you must definitely train and maintain these skills consistently.


This method is based on the distillation of water using solar radiation. This technique requires the manufacturing process of the above device but can provide drinking water for a long time without any special maintenance. Another method is to collect moisture from the vegetation. You see, we can do that later. The bag must be transparent to allow sunlight to enter. Regarding the pipe, the use of a surgical pipe is recommended and we should know that the water will have a slight taste of the smell of the vegetation from where it came from. In this method we must be careful not to use it on poisonous or toxic plants. In areas with more intense vegetation we can do the same with a tree as you see below.


Similar to the technique near shores, we can use natural soil filtration in swamps with the method you see in the image below. Just like water collection techniques, there are just as many techniques for filtering water. The principle is that we want to pass water through porous materials (sand, coals, leaves, etc.) to remove as much as possible harmful particles as possible. Always, the safest method is to boil the water for at least one minute.


The issue of water in survival is a matter of the utmost importance and the more we know the better our chances of survival. As in all subjects, theoretical knowledge without practice and repetition has very little value. So, if you are interested in this subject, you must definitely train and maintain these skills consistently.
 In extreme survival situations everyone suggests short-term survival kits, we will break the established and suggest in your survival kit to include long-term survival items such as small farm tools such as small pickaxe, spade shovel, split saw (initially can be used for cutting and for defense) , but later in combination with a set of SEED PACKAGE of all kinds can be the key to surviving away from dangerous urban centers.
In extreme survival situations everyone suggests short-term survival kits, we will break the established and suggest in your survival kit to include long-term survival items such as small farm tools such as small pickaxe, spade shovel, split saw (initially can be used for cutting and for defense) , but later in combination with a set of SEED PACKAGE of all kinds can be the key to surviving away from dangerous urban centers.Free Crisis Survival Books


Most are offered free of charge by foreign or Greek digital libraries, Universities, organizations, or by their creators and are for personal use only. The books are for information only and the website is not responsible for their content. If any of the book links do not work and do not refer you to this book, please let me know by sending a message here, or by email to ftiaxnw@gmail.com , to check it out. How to survive financially
Overcome the Financial Crisis! The times are so difficult that we have to download ideas to survive.
General Survival
3 Day Emergency Preps
72 Hour Supplies
All Hazard Preparedness Workbook
Common Sense Guide To Being Prepared
Compact Survival Kit
Complete Worst Case Scenario
Disaster Handbook
Emergency Preparedness Checklist
Emergency Preparedness Manual
Emergency Supplies Checklist
FEMA - Are You Ready?
FRC Preparedness Handbook
How to Prepare for Any Disaster
LA Fire Department Emergency Preparedness
Mini Urban Survival Kit
National Security Emergencies
Ragnar’s Urban Survival
Surviving in the City
Communication
Bass Pro Shop Radio Guide
Best Buy FRS Radio Guide
Disaster Communications
Disaster Communications 2
Hams to the Rescue
How to Buy a Two Way
Radio Amateur's Handbook
Radio Info
Reconnecting After Disaster
Shortwave Radio 101
Shortwave Radio Handbook
Survival Communication 101
Survival Communications Primer
Cook Books
Belgian Cook Book
Cloud City Cookbook
Genesee Valley Cookbook
Kenton Cookbook
Modern Women of America Cookbook
Most For Your Money
Native American Health Recipes
Pleasantville Cook Book
Riverside Recipe Book
Second Parish Cookbook
Vegetarian Cook Book
Westminster Cook Book
Cooking Methods
Base Camp Trail Stove
Bush Fungus Stove
Double Drum Sawdust Stove
Emergency Bread
Food Bucket Stove
Rocket Stove
Sawdust Burning Stove
Energy, Fire, Light
Biodiesel Safety
Bow Drill
Cheat Solar Power
Choosing a Back Up Generator
Emergency Power Options
Fighting Fire
Fire by Can
Generator Sizing WP
Getting Started In Solar
Homemade Windmills
How Much Is Enough
Making Charcoal
Power Outage Checklist
Solar Power
Solar Water Heater
SunWize RVkits specsheet
Tinder Fungus
Water Proof Matches
Food and Storage
3 Month Supply Of Food
Emergency Food and Water
Emergency Food for Babies
Emergency Preparedness Food
Family Food Storage
Food Storage for 1 Year
Food Storage for Survival
Food Storage Guide
Food Storage in the Home
Food Storage and Rodents
Get Ready Now
Grain Dehuller
Grain Thresher
Grains And Legumes
Growing and Harvesting Wheat
Hand Operated Winnower
Improvised Grain Mill
Keeping Food Safe to Eat
Mylar Bag Sealing Methods
One Year Emergency Food Supply
Peddle Operated Grain Mill
Plant Identification
Preserving Vegetables
Shelf Life of Food Storage
Stocking Food
Stocking For Small Spaces
Storage of Wheat
Survival Food Storage
TACDA Emergency Food and Water
Vacuum Packing Seed
Gardening
A Better Way to Gardening
Amateur Garden
Building a Hydroponic Garden
Container Gardening 1
Container Gardening 2
Container Gardening Vegetables
Growing Container Vegetables
Growing Mini Gardens
Growing Sweet Corn
Growing Vegetables at Home
Growing Vegetables Basics
Growing Vegetables from Seed
Growing Vegetables in Containers
Keeping Food Safe in an Emergency
NC State - Growing Vegetables
NC State - Home Vegetables
Raised Bed Gardening
Short Season Vegetable Gardening
SM Space Gardening
Small Plastic Greenhouses
Start a Small Garden
Start a Vegetable Garden
Start Garden Transplants
Vegetable Gardening Encyclopedia
Health, Medical, Sanitation
Animal Bites First Aid
Base Campe Hygiene and Health
Blisters First Aid
Burns First Aid
CPR Instructions
Diabetes Disaster Guidelines
Edible Medicinal Plants
Emergency War Surgery
First Aid For Soldiers
Isolation Planning
Mass Casualty Planning
Medical emergencies
Medical NBC Battlebook
Survival Medicine
Survival Wilderness Medicine
the Using Safe Burial Practices
Wilderness Med Kit
Nuclear, Biological, Chemical
CBR Nuclear War Survival
Chemical emergencies
EMP Commission 7MB
EMP Executive Report Report
Fallout Protection
FEMA CBR Nuclear War Survival
FEMA Nuclear Survival
Nuclear War Survival Skills
Nuclear Weapons Effects
Radiological Defense Preparedness
SM-12f Home Fallout Shelter
Threat to US from an EMP Attack
What if Nuclear War is Imminent
Official Manuals
Canada CD Notebook
Canada CD Operations
Canada CD Public Information
FM 3-06 Urban Combat
FM 3-3-1 Nuclear Contamination
FM 3-4 NBC Protection
FM 3-5 NBC Decontamination
FM 3-9 Chemical / Biological
FM 3-11-4 Mulitiservice Tactics
FM 4-02 Nuclear Casualties
FM 4-25-11
FM 5-20 Camouflage
FM 7 NBC Field Handbook
FM 8-50 Bandaging
FM 8-284 Treatment of Casualties
FM 21-10 Field Hygeine
FM 21-11 First Aid for Soldiers
FM 21-75 Combat Skills
FM 21-76 Survival Manual
FM 21-150 Combatives
FM 90-10-1 Combat
US Army Dairy
United States Marine Survival
US Marine Corps MCRP 3-02F
US Marine Corps MSVX.02.01
Self Defense, Weapons
Choosing a Weapon
Citizen’s Homeland Defense Guide I
Citizen’s Homeland Defense Guide II
FN High Capacity 45
G&A SR9
Glock Versus M1911
Homeland Defense 45
Military Operations On Urbanized Terrain
Smith & Wesson Sigma SW9VE
Springfield XD Review
Ruger SR9
Stag Review
Survival Guns
Survival Weapons
Tactical Ready Guide
Shelter
Basement Shelter
Build a Fallout Shelter
Build a Shelter
Home Shelter Above Ground
Home Shelter Outside Concrete
Shelter Management Handbook
Shelters
Survival Wilderness Shelter Types
Taking Shelter
Wilderness Shelter Types
Water
Emergency Disinfection of Water
Emergency Water Purification
Priming the Berkey Filter
Purification Of Water On A Small_Scale
Purify Water in an Emergency
Solar Photovotaics
Solar Water Heater
Water Survival Course
Water Treatment
Wind Machine for Pumping Water
Miscellaneous
Art and Science of Dumpster Diving
BOB Survival Kit
Bug Out Bag
Bug Out Vehicle Basics
Desert Survival
Earthquake Preparedness Guide
Earthquake Tips
Get Out Of Dodge
Handbook of Knots and Splices
How to Avoid Getting Lost
How To Find Your Way
Knots For Camping Climbing Utility
Pioneering Knots and Lashings
Poisonous Plants
Wilderness Survival Techniques
Winter Survival
Winter Survival In Your Car
Read more: Free books for materials and constructions
http://7lt-laris.lar.sch.gr/OLYMPOS/OLYMPOS%20CD/files/ol_atyximata_files/random.pdf
http://antikatanalotis.blogspot.gr/2013/04/blog-post_7801.html
http://ofis66.blogspot.gr/2014/05/blog-post_5.html#axzz49YftPRTGhttp://antikatanalotis.blogspot.gr/2013/04/blog-post_7801.html
http://www.parnitha‐np.gr/oreivasia.htm
http://www.hellaspath.gr/index.php? p = 2
http://greekcitizen.pblogs.gr/odhgies-epibiwshs-ellhnwn-labete-ta-metra-sas-gia-kathe-endehome.html
http://apocalypsejohn.com/odigos-epiviosis-katastasi-polemou/
http://pseed.gr/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=7623%3A2015-11-11-00-33-05&catid=82% 3A2012-12-05-14-16-01 & Itemid = 470
http://periergaa.blogspot.gr/2016/03/blog-post_156.html
http://patari.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=14231&sid= 1b818e0ae7cc291c771aab05b0478f4c
http://www.epsilonellas.gr/2015/01/blog-post_54.html
http://luben.tv/politix/75101
http://www.pronews.gr/
http: /2014/05/blog-post_3841.html
https://laspas.gr/2013/05/12/odigos-epiviosis/
http://katohika.gr/gn-blog/odigos-epiviosis-empolemon/
http: // 7lt-laris.lar.sch.gr/OLYMPOS/OLYMPOS%20CD/files/ol_atyximata_files/random.pdf
http://diaviosi.blogspot.gr/2013/10/fotia.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YBZOeJH91Ko
http://pseed.gr/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=7623%3A2015-11-11-00-33-05&catid=82% 3A2012-12-05-14-16-01 & Itemid = 470
http://periergaa.blogspot.gr/2016/03/blog-post_156.html
http://patari.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=14231&sid= 1b818e0ae7cc291c771aab05b0478f4c
http://www.epsilonellas.gr/2015/01/blog-post_54.html
http://luben.tv/politix/75101
http://www.pronews.gr/
http: /2014/05/blog-post_3841.html
https://laspas.gr/2013/05/12/odigos-epiviosis/
http://katohika.gr/gn-blog/odigos-epiviosis-empolemon/
http: // 7lt-laris.lar.sch.gr/OLYMPOS/OLYMPOS%20CD/files/ol_atyximata_files/random.pdf
http://diaviosi.blogspot.gr/2013/10/fotia.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YBZOeJH91Ko





Post a Comment